Basics and motivation#
Questions
What is version control and why?
What are commits and branches?
What are forks and clones?
Objectives
Get a mental representation for commits and branches.
Understand the difference between forks and clones.
Understand the difference between Git and GitHub.
What we will not cover
Command line interface
Cloning using SSH protocol and SSH keys
Rebasing and squashing
Many Git tricks which can be explored later
Version control#
What are version control tools?#
Version control is a tool that can record snapshots of a project.
You can think of version control like regularly taking a photo of your work (movie sets take regular polaroids to be able to recreate a scene the next day).
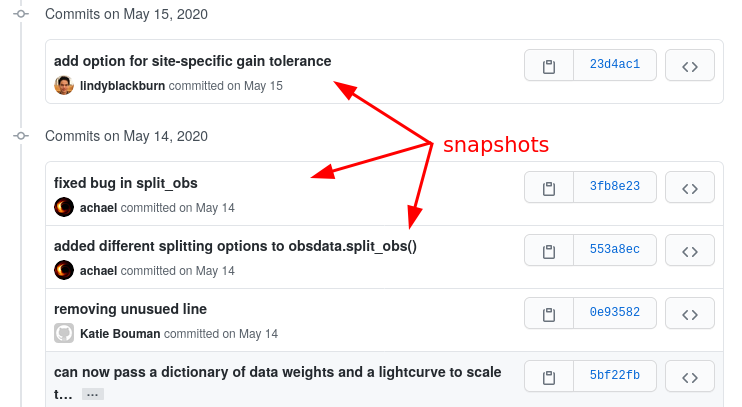
Fig. 1 Snapshots (commits) in the EHT-imaging repository.#
What we typically like to snapshot#
Software (this is how it started but Git/GitHub can track a lot more)
Scripts
Documents (plain text file much better suitable than Word documents)
Manuscripts (Git is great for collaborating/sharing LaTeX manuscripts)
Configuration files
Website sources
Data
Why are snapshots valuable? Reproducibility!#
We can always go back if we make a mistake.
We have the means to refer to a well-defined version of a project when sharing, collaborating, and publishing.
If we discover a problem, we can find out when it was introduced.
Difference between Git and GitHub#
Git
Tool that can record and synchronize snapshots.
Not the only tool that can record snapshots (other popular tools are Subversion and Mercurial).
Not only a tool but also a format that can be read by many different tools.
GitHub
Service that provides hosting for Git repositories with a nice web interface.
Not the only service that provides this (other popular services are GitLab and Bitbucket).
GitHub Desktop
Graphical user interface to Git and GitHub which runs locally on your computer.
There are other tools that can do this, too (e.g. Sourcetree).
Commits, branches, repositories, forks, clones#
repository: The project, contains all data and history (commits, branches, tags).
commit: Snapshot of the project, gets a unique identifier (e.g.
c7f0e8bfc718be04525847fc7ac237f470add76e).branch: Independent development line, often we call the main development line
master.tag: A pointer to one commit, to be able to refer to it later. Like a sticky note that you attach to a particular commit (e.g.
phd-printedorpaper-submitted).cloning: Copying the whole repository to your laptop - the first time. It is not necessary to download each file one by one.
forking: Taking a copy of a repository (which is typically not yours) - your copy (fork) stays on GitHub and you can make changes to your copy.
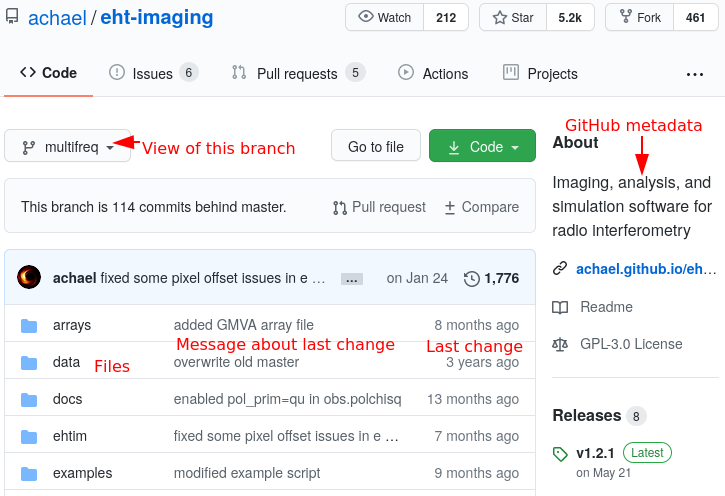
Fig. 2 GitHub file view of the EHT-imaging repository. This is the version of all files at a single point in time.#
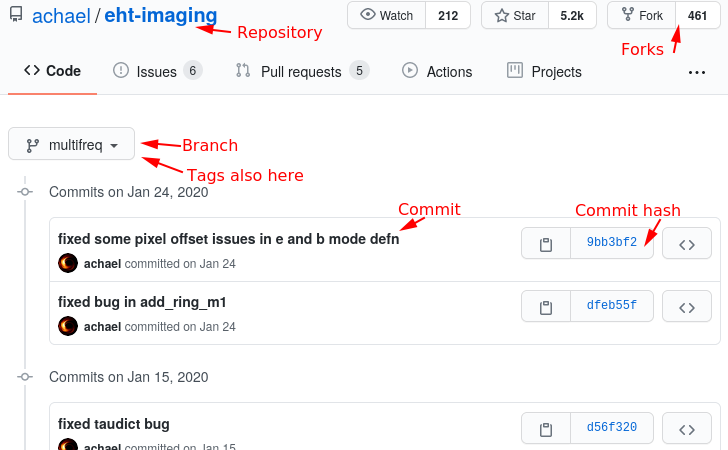
Fig. 3 Github history view of the EHT-imaging repository. This is the progression of the repository (with the commit message over time).#
Fig. 4 Network graph of all commits in the EHT-imaging repository. This shows the relationship between different forks of people who are contributing and sharing code.#
Interesting repositories to explore these concepts#
Event Horizon Telescope imaging software
Repository: achael/eht-imaging
Commits, branches, forks: achael/eht-imaging
-
Contains data and code necessary to create figures from their article.
FiveThirtyEight story Why We’re Sharing 3 Million Russian Troll Tweets
Contains data and readme file, no code.
The NY Times Coronavirus (Covid-19) Data in the United States
Contains data, readme, license, but no code. As of 2020.april, being updated every day.
Data: nytimes/covid-19-data
Website: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/us/coronavirus-us-cases.html
CSV exports of the Getty Provenance Index
Entire books are written using Git/GitHub:
Papers under open review:
Discussion#
Why use repositories?
All changes are recorded.
We do not have to send changes via email.
We can experiment with several ideas which might not work out (using branches).
Several people can work on the same project at the same time (using branches).
We do not have to wait for others to send us “the latest version” over email.
We do not have to merge parallel developments by hand.
Group-based access model where shared access is the default, instead of everything fundamentally owned by individuals who manage sharing as-needed: with Git you can easily have collaboration be the default.
It is possible to serve websites directly from a repository.
Discussion
How have you solved these in the past without version control?